rocketmq分享
版权声明 本站原创文章 由 萌叔 发表
转载请注明 萌叔 | https://vearne.cc
注意:文中使用的部分图,误将ConsumeQueue写成了ConsumerQueue
1.简介
RocketMQ是一个分布式消息和流数据平台,具有低延迟、高性能、高可靠性、万亿级容量和灵活的可扩展性。RocketMQ是2012年阿里巴巴开源的第三代分布式消息中间件,2016年11月21日,阿里巴巴向Apache软件基金会捐赠了RocketMQ;第二年2月20日,Apache软件基金会宣布Apache RocketMQ成为顶级项目。
2.架构
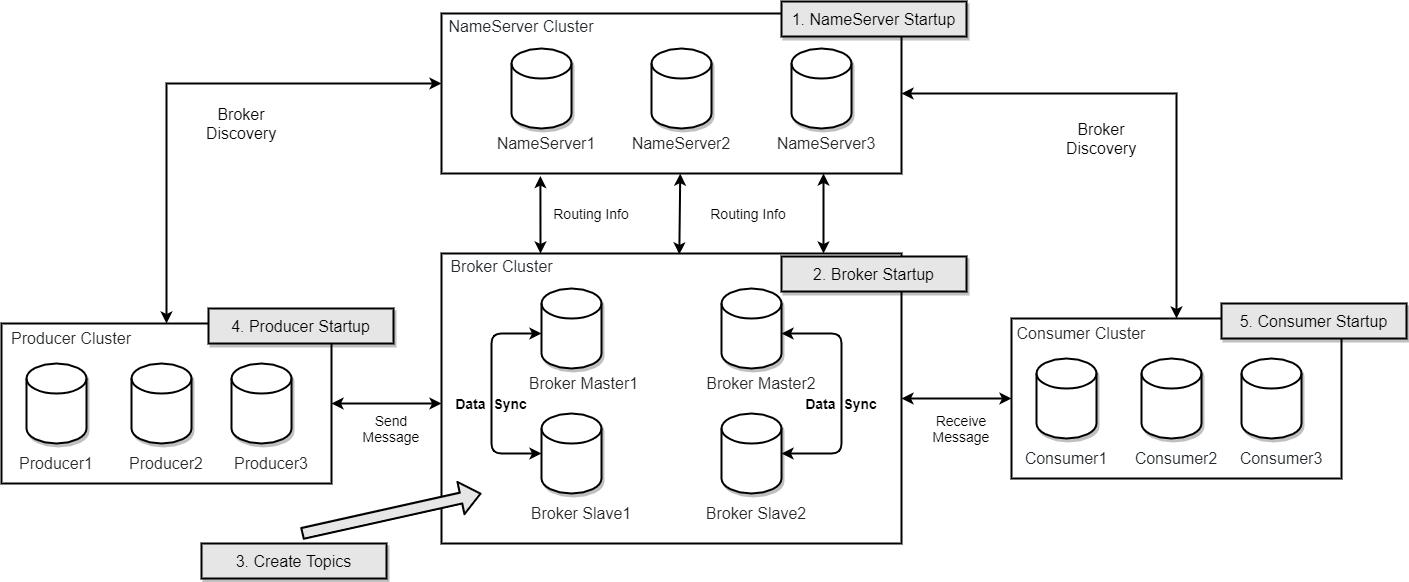

正常情况,写和读都走Master,Master如果宕机,读可以走Slave
在 RocketMQ 4.5 版本之前,RocketMQ 只有 Master/Slave 一种部署方式,虽然这种模式可以提供一定的高可用性但也存在比较大的缺陷。为了实现新的高可用多副本架构,RockeMQ 最终选用了基于 Raft 协议的 commitlog 存储库 DLedger。
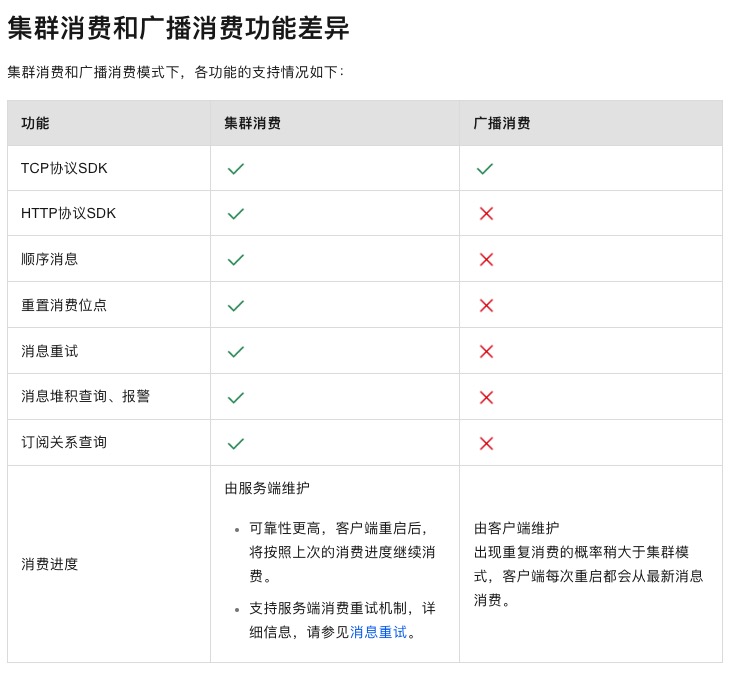
2.1 四种角色
2.1.1 NameServer
存储元数据 topic -> broker
- 无状态
- 接收来自broker的心跳
- 检查与borker的通讯是否过期
Topic路由信息
{
"OrderTopicConf": "",
"queueDatas": [{
"brokerName": "broker-3",
"readQueueNums": 4,
"writeQueueNums": 4,
"perm": 6,
"topicSynFlag": 0
}, {
"brokerName": "broker-4",
"readQueueNums": 4,
"writeQueueNums": 4,
"perm": 6,
"topicSynFlag": 0
}],
"brokerDatas": [{
"cluster": "Default_Cluster",
"brokerName": "broker-4",
"brokerAddrs": {
"0": "192.168.12.123:10911",
"1": "192.168.12.127:10911"
}
}, {
"cluster": "Default_Cluster",
"brokerName": "broker-3",
"brokerAddrs": {
"1": "192.168.12.220:10911",
"0": "192.168.12.12:10911"
}
}]
}
2.1.2 Producter
有发往broker的心跳(Master)
{
"clientID": "192.168.20.139@67576",
"producerDataSet": [{
"groupName": "PG-test"
}],
"consumerDataSet": []
}
2.1.3 Consumer
每30秒
有发往broker的心跳(Master)
* 注意下面有2个Topic
{
"clientID": "192.168.20.139@05B75F58-C651-451D-A5BE-5E7D3E388373",
"producerDataSet": [],
"consumerDataSet": [{
"groupName": "CG-test",
"consumeType": "CONSUME_PASSIVELY",
"messageModel": "CLUSTERING",
"consumeFromWhere": "CONSUME_FROM_FIRST_OFFSET",
"subscriptionDataSet": [{
"classFilterMode": false,
"topic": "helloworld",
"subString": "tag2",
"tagsSet": ["tag2"],
"codeSet": ["3552216"],
"subVersion": 1637657077446848000,
"expressionType": "TAG"
}, {
"classFilterMode": false,
"topic": "%RETRY%CG-test",
"subString": "*",
"tagsSet": [],
"codeSet": [],
"subVersion": 1637657077514551000,
"expressionType": "TAG"
}],
"unitMode": false
}]
}
2.1.4 Broker
MessageQueue
- MessageQueue类似于kafka中的partition
- MessageQueue的唯一坐标是topic -> brokerName -> queueId

存储实际的消息数据
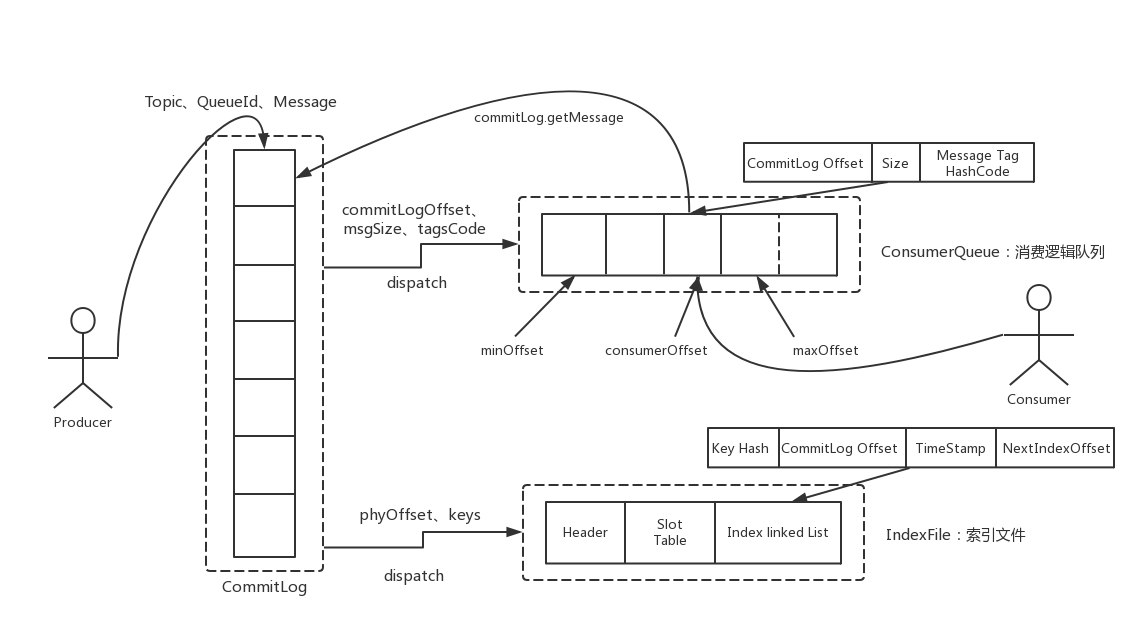
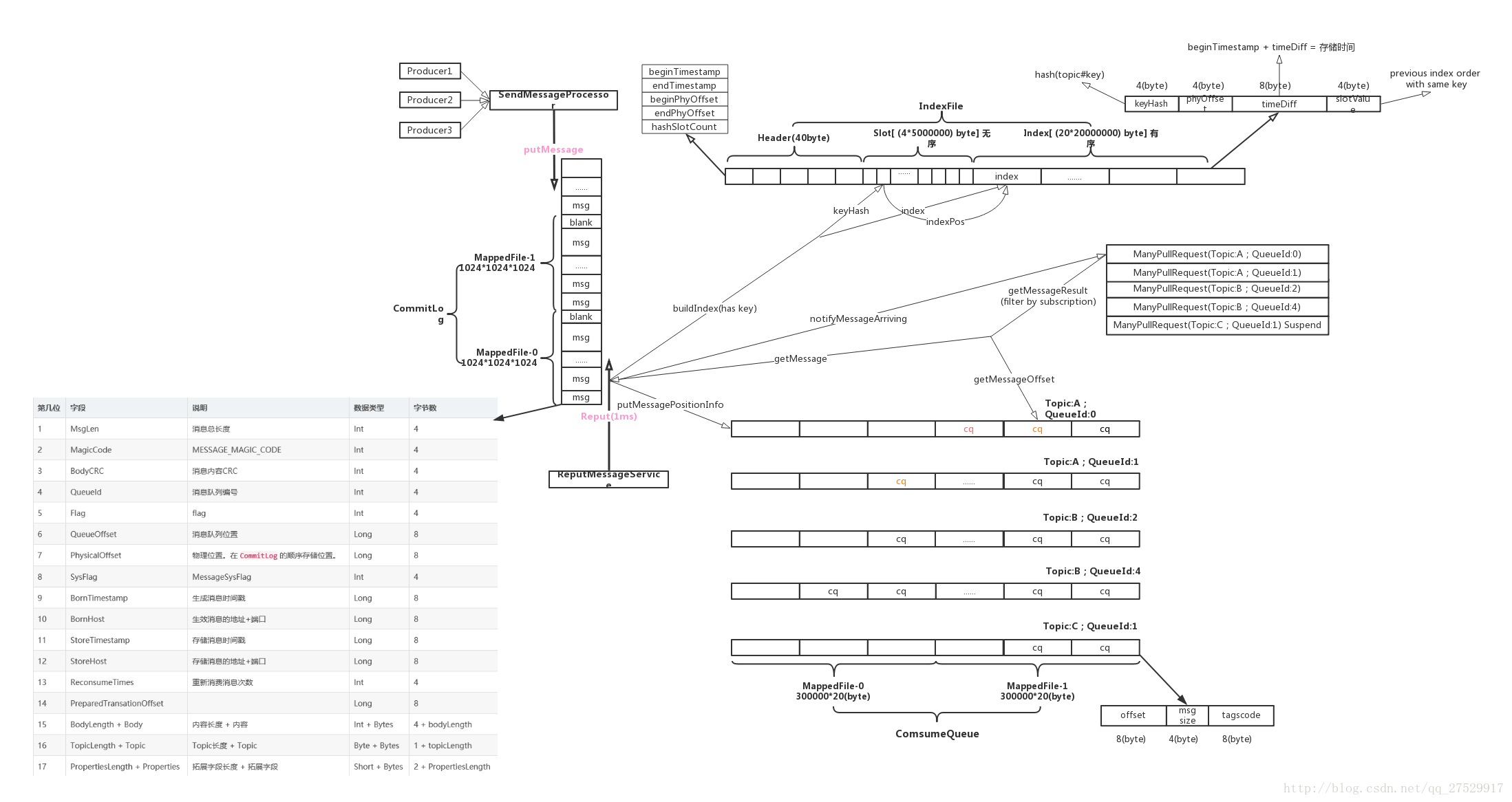
三种文件
- commitLog 顺序写的文件
- indexFile 索引
- consumeQueue 索引
2.1.4.1 注意与kafka的差异
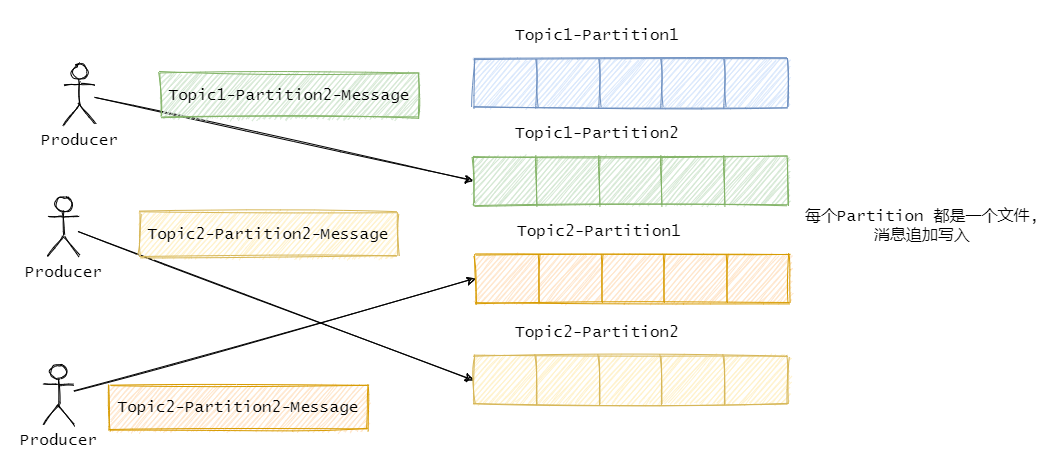
topic -> partition -> segment
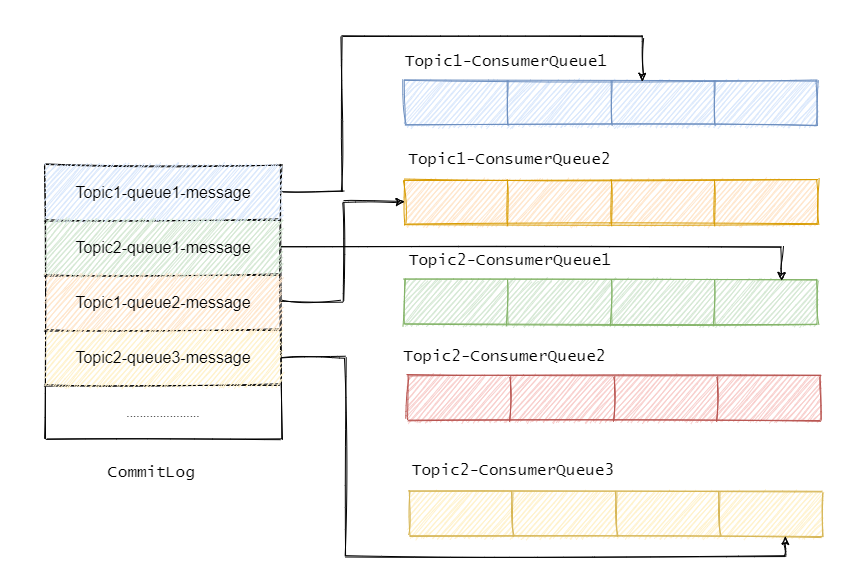
多个topic共用commitLog
Why?
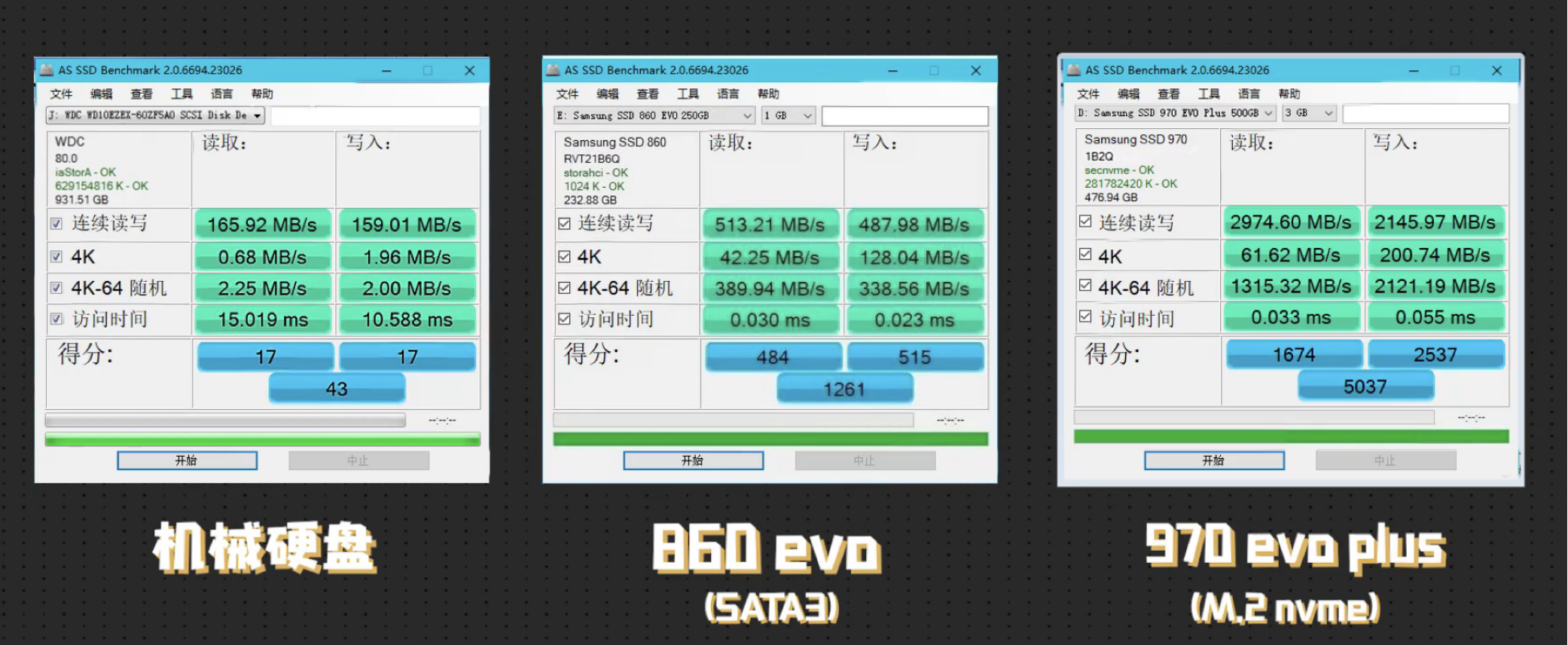
注意: 分区多文件多,那么局部的顺序读写会退化到随机IO
3.特性&新概念
3.1 订阅与发布
3.2 消息顺序
- 分区顺序
- 全局顺序
全局顺序消息实际上是一种特殊的分区顺序消息,即Topic中只有一个分区,因此全局顺序和分区顺序的实现原理相同。因为分区顺序消息有多个分区,所以分区顺序消息比全局顺序消息的并发度和性能更高。
3.3 2种消费方式
- ConsumeMode.ORDERLY
- ConsumeMode.CONCURRENTLY
涉及特殊的Command和线程池
ReqLockBatchMQ = int16(41)
ReqUnlockBatchMQ = int16(42)
3.4 消息过滤
- 支持SQL92和Tag 2种方式
- Tag过滤会在broker段和consumer端各过滤一次
3.5 至少一次
3.6 回溯消费
3.7 事务消息
3.8 定时消息
3.9 消息重试&重投
3.10 消息类型
- sync
- async
- oneway
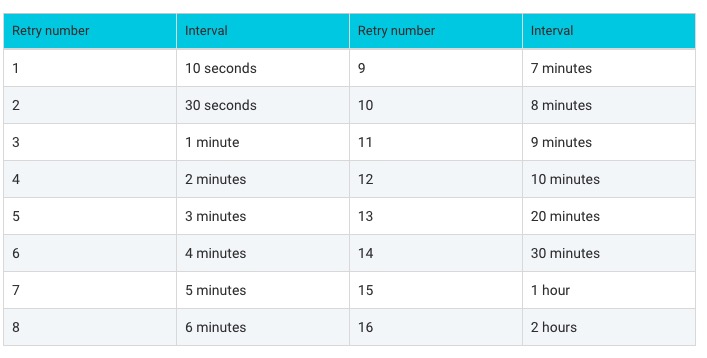
4.延迟&重试机制
4.1 延迟
- 不支持任意时时延的消息
- 18个延迟级别
messageDelayLevel="1s 5s 10s 30s 1m 2m 3m 4m 5m 6m 7m 8m 9m 10m 20m 30m 1h 2h"
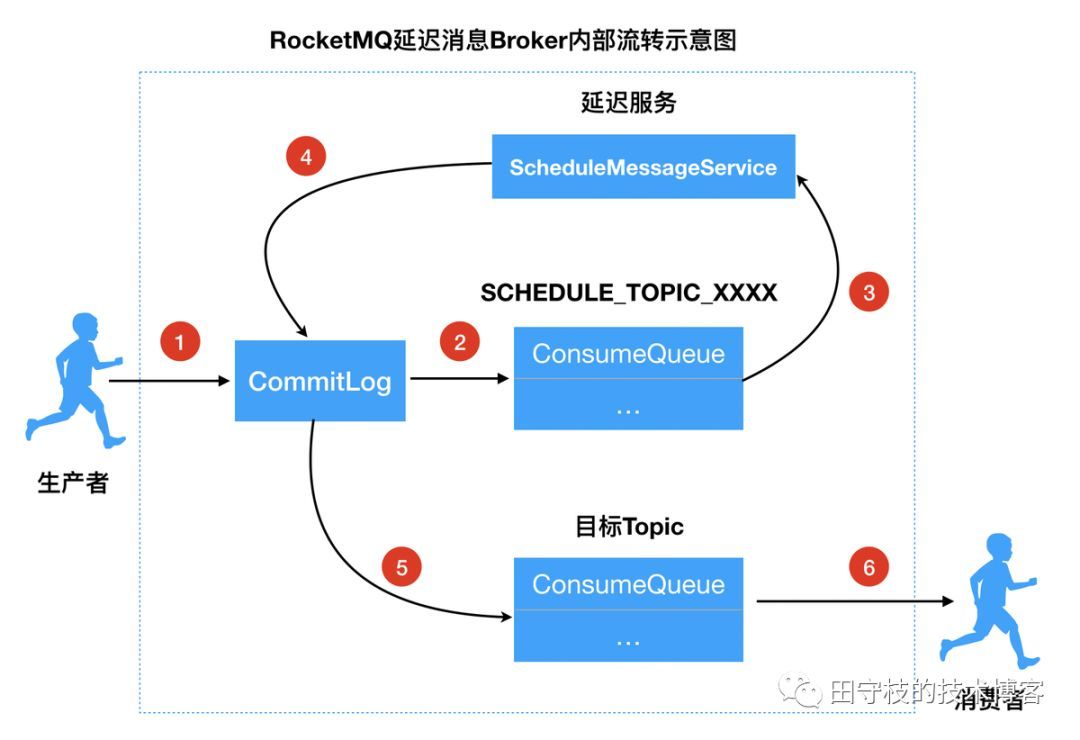
1) 修改消息Topic名称和队列信息
2) 转发消息到延迟主题的CosumeQueue中
3) 延迟服务消费SCHEDULE_TOPIC_XXXX消息
4) 将信息重新存储到CommitLog中
5) 将消息投递到目标Topic中
6) 消费者消费目标topic中的数据
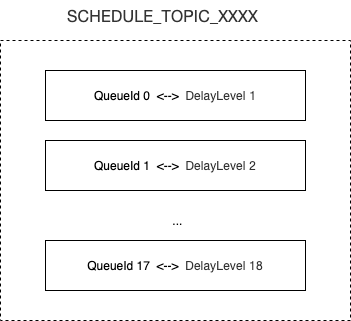
SCHEDULE_TOPIC_XXXX中的每个ConsumeQueue都相当于QelayQueue
4.2 重试
err := c.Subscribe(TopicName,
consumer.MessageSelector{Type: consumer.TAG, Expression: "tag1||tag2"},
func(ctx context.Context,
msgs ...*primitive.MessageExt) (consumer.ConsumeResult, error) {
cCtx, _ := primitive.GetConcurrentlyCtx(ctx)
//cCtx.DelayLevelWhenNextConsume = delayLevel // only run when return consumer.ConsumeRetryLater
fmt.Println("DelayLevelWhenNextConsume", cCtx.DelayLevelWhenNextConsume)
for i, msg := range msgs {
counter++
fmt.Println("ReconsumeTimes", msg.ReconsumeTimes, "BornTimestamp", msg.BornTimestamp)
fmt.Println("topic", msg.Topic)
fmt.Println(string(msg.Body))
fmt.Println("tags:", msg.GetTags())
fmt.Printf("subscribe callback: %v, counter:%v \n", msgs[i], counter)
}
return consumer.ConsumeRetryLater, nil
//return consumer.ConsumeSuccess, nil
})
ReqConsumerSendMsgBack = int16(36)
- 消息再次收到来自%RETRY%{consumerGroup}
- 如果多次重试还是无法成功,会进入死信队列 %DLQ%{consumerGroup}
5.负载均衡
5.1 触发时机
- client启动时
- 定时20s检查是否需要负载均衡
- broker推送通知 ReqNotifyConsumerIdsChanged
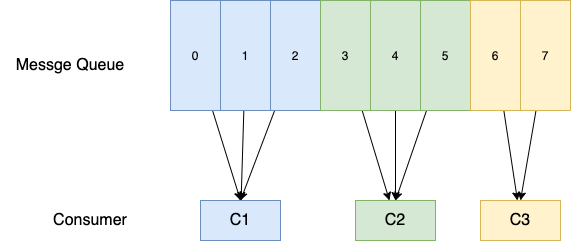
5.2 具体步骤
1)获取MessageQueue List
- 从NameServer获取
- 排序
[topic=helloworld, brokerName=broker-3, queueId=0]
[topic=helloworld, brokerName=broker-3, queueId=1]
[topic=helloworld, brokerName=broker-3, queueId=2]
[topic=helloworld, brokerName=broker-3, queueId=3]
[topic=helloworld, brokerName=broker-4, queueId=0]
[topic=helloworld, brokerName=broker-4, queueId=1]
[topic=helloworld, brokerName=broker-4, queueId=2]
[topic=helloworld, brokerName=broker-4, queueId=3]
2)获取ConsumerList
- 从Broker获取
- 排序
192.168.100.20@24758
192.168.100.21@33922
3) 根据某种策略来计算自己的负载
- AllocateByAveragely
- AllocateByAveragelyCircle
- AllocateByMachineNearby
- AllocateByConfig
- AllocateByMachineRoom
- AllocateByConsistentHash
以AllocateByAveragely 举例
5.3 缺陷
- 重复消费
6.数据存储
7.数据查询
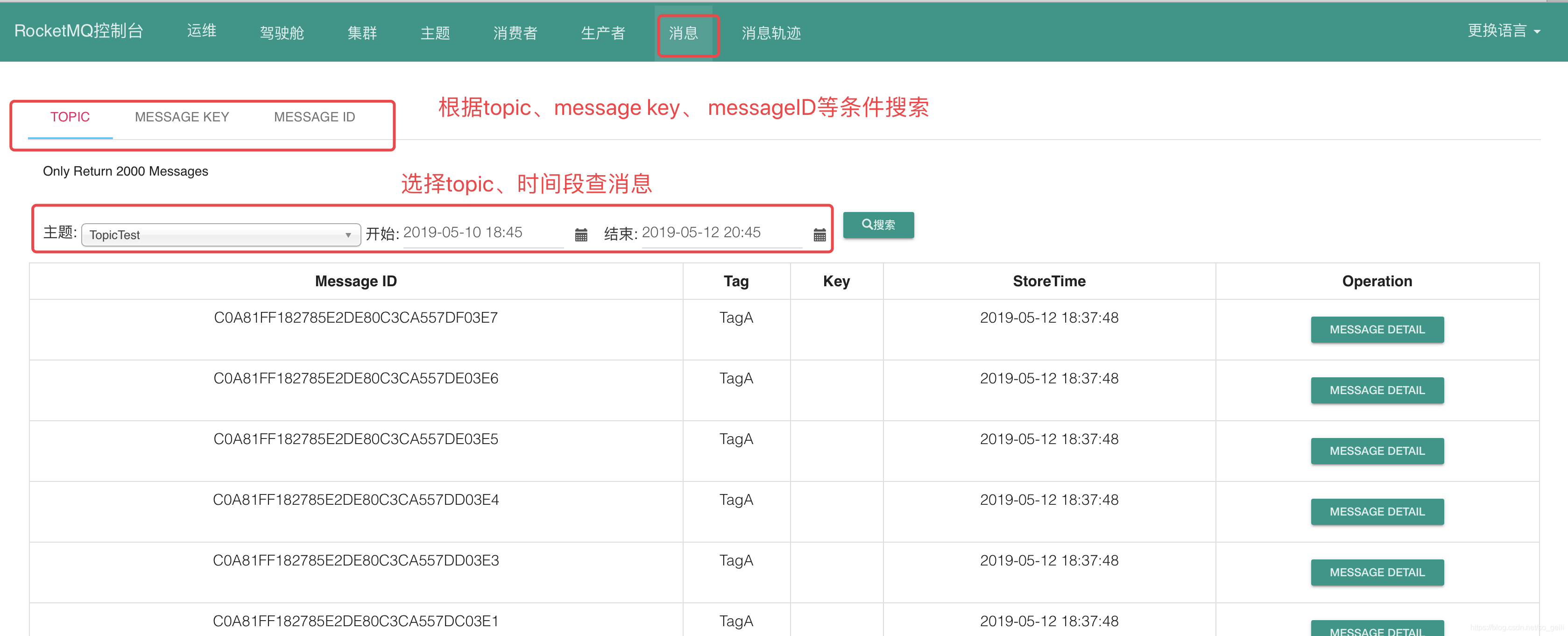
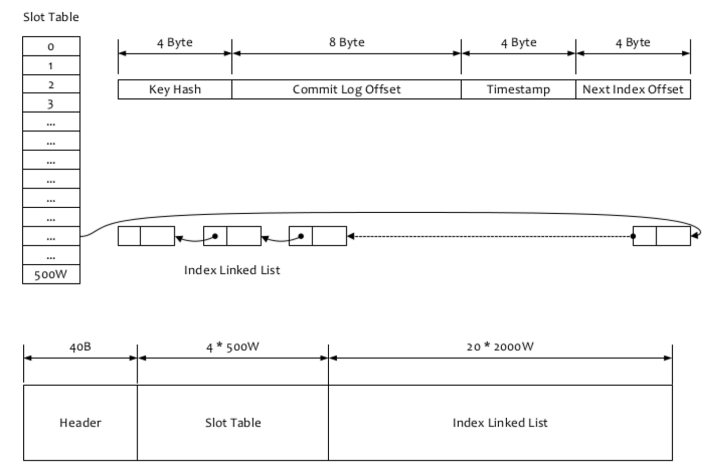
7.1 按照msgID查询
7.1.1 msgId和offsetMsgId
msgId 客户端生成 也叫做"UNIQ_KEY"
该ID 是消息发送者在消息发送时会首先在客户端生成,全局唯一
offsetMsgId 服务端生成的
该ID 是消息发送者在消息发送时会首先在客户端生成,全局唯一,在 RocketMQ 中该 ID 还有另外的一个叫法:uniqId,无不体现其全局唯一性。
offsetMsgId:消息偏移ID,该 ID 记录了消息所在集群的物理地址,主要包含所存储 Broker 服务器的地址( IP 与端口号)以及所在commitlog 文件的物理偏移量。
解析offsetMsgId获取broker的地址和phyOffset
此处phyOffset是commitLog(多个文件分片都是定长)的文件偏移量
7.2 按照Topic+key查询
1条消息可以产生多条索引
topic + # + 消息的 key --> commitLogOffset
topic + # + uniqKey --> commitLogOffset
7.3 按照Topic+queueID + beginTimestamp + EndTimestamp
7.3.1 通过beginTimestamp获得consumeQueue中的minOffset
- 根据beginTimestamp比对consumeQueue(多个文件分片)的LastModifiedTime,确定文件分片
- 使用二分查找获得minOffset,过程中需要从commitLog获得StoreTimeStamp
7.3.2 通过EndTimestamp获得consumeQueue中maxOffset
7.3.3 按照Topic+queueID+minOffset+maxOffset读取消息
参考资料
1.RocketMQ吐血总结
2.rocketMq-Topic创建过程
3.RocketMQ源码分析:Broker心跳原理
4.RocketMQ——通信协议
5.RocketMq 消息Tag过滤
6.RocketMQ msgId与offsetMsgId释疑(实战篇)
7.源码分析RocketMQ之消费队列、Index索引文件存储结构与存储机制-上篇
8.源码分析RocketMQ之消费队列、Index索引文件存储结构与存储机制-下篇
9.深入理解RocketMQ延迟消息
10.Kafka和RocketMQ底层存储之那些你不知道的事
11.集群消费和广播消费
后记
2023年11月30日, Rocketmq支持在广播模式下,多个消费者使用相同的GroupName。
但是需要注意server端不存储consumer的offset,也就是说无法记录consumer的消费进度。
其实也比较好理解,多个消费者用同一个GroupName, 那么到底该存哪一个?所以干脆都不存。