聊聊Gossip的一个实现
版权声明 本站原创文章 由 萌叔 发表
转载请注明 萌叔 | https://vearne.cc1. 引言
Gossip是一种去中心化、容错并保证最终一致性的协议。它的基本思想是通过不断的和集群中的节点gossip交换信息,经过 O(log(n))个回合, gossip协议即可将信息传递到所有的节点。
这里介绍Gossip的一个实现库hashicorp/memberlist,并讲一下需要注意的事项。
2. hashicorp/memberlist
memberlist是HashiCorp公司开源的Gossip库,这个库被consul(也是HashiCorp公司开源的)所引用。
它是SWIM的一个扩展实现。
下面的例子test_gossip.go中它被用来做集群节点发现
package main
import (
"flag"
"fmt"
"github.com/hashicorp/memberlist"
// "net"
"os"
"strconv"
"time"
)
var (
bindPort = flag.Int("port", 8001, "gossip port")
)
func main() {
flag.Parse()
hostname, _ := os.Hostname()
config := memberlist.DefaultLocalConfig()
config.Name = hostname + "-" + strconv.Itoa(*bindPort)
// config := memberlist.DefaultLocalConfig()
config.BindPort = *bindPort
config.AdvertisePort = *bindPort
fmt.Println("config.DisableTcpPings", config.DisableTcpPings)
fmt.Println("config.IndirectChecks", config.IndirectChecks)
fmt.Println("config.RetransmitMult", config.RetransmitMult)
fmt.Println("config.PushPullInterval", config.PushPullInterval)
fmt.Println("config.ProbeInterval", config.ProbeInterval)
fmt.Println("config.GossipInterval", config.GossipInterval)
fmt.Println("config.GossipNodes", config.GossipNodes)
fmt.Println("config.BindPort", config.BindPort)
list, err := memberlist.Create(config)
if err != nil {
panic("Failed to create memberlist: " + err.Error())
}
// Join an existing cluster by specifying at least one known member.
// 配置种子节点, 这里我直接写死了
_, err = list.Join([]string{"127.0.0.1:8001", "127.0.0.1:8002"})
fmt.Println("err", err)
if err != nil {
panic("Failed to join cluster: " + err.Error())
}
// Ask for members of the cluster
for {
fmt.Println("-------------start--------------")
for _, member := range list.Members() {
fmt.Printf("Member: %s %s\n", member.Name, member.Addr)
}
fmt.Println("-------------end--------------")
time.Sleep(time.Second * 3)
}
}可以直接在单机上进行测试,启动
go run test_gossip.go --port 8001
go run test_gossip.go --port 8002
go run test_gossip.go --port 8003程序会不断在窗口打印发现的所有集群节点, 形如
-------------start--------------
Member: MacBook-Pro.local-8002 192.168.13.110
Member: MacBook-Pro.local-8001 192.168.13.110
Member: MacBook-Pro.local-8003 192.168.13.110
-------------end--------------如果需要做其它信息交换,请阅读参考资料2
3. 基本过程
3.1 状态
节点的state有3种
alive 节点是"活的"
suspect 对于PingMsg没有应答或应答超时,这个节点的状态是"可疑的"
dead 节点"已死亡"
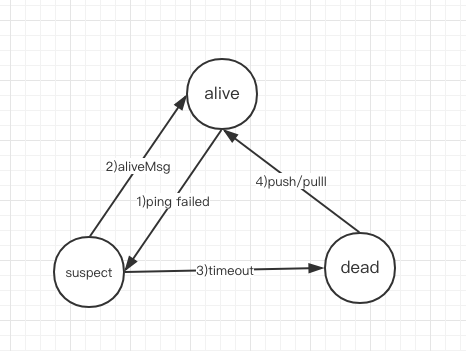
1) 如果节点B无法被对节点A发出的PingMsg(这里是作者自定义的UDP协议,不是ICMP)进行响应,或者响应超时,它会被节点A标为suspect, 如果suspect持续一段时间(或它收到足够多的其它节点关于B的SuspectMsg),节点A会在集群中广播SuspectMsg,告知集群中的其它节点,节点B很可疑
2)如果B收到了针对它的SuspectMsg,这显然是对它的不利言论,B可以通过发送AliveMsg告知对方, "I'm alive"。那么在对方节点看来B的state从suspect变为alive
3) 如果一段时间内,B的状态仍然是suspect, 那么对节点A而言,B的状态会被置为dead
4) 如果节点B在down掉一段时间后,重新上线,它可以通过与种子节点的Gossip(push/pull) 重新被认为alive
3.2 动作
memberlist所有动作都可以在schedule()看到, 动作共有3种
state.go
// Schedule is used to ensure the Tick is performed periodically. This
// function is safe to call multiple times. If the memberlist is already
// scheduled, then it won't do anything.
func (m *Memberlist) schedule() {
m.tickerLock.Lock()
defer m.tickerLock.Unlock()
// If we already have tickers, then don't do anything, since we're
// scheduled
if len(m.tickers) > 0 {
return
}
// Create the stop tick channel, a blocking channel. We close this
// when we should stop the tickers.
stopCh := make(chan struct{})
// Create a new probeTicker
if m.config.ProbeInterval > 0 {
t := time.NewTicker(m.config.ProbeInterval)
// 动作1
go m.triggerFunc(m.config.ProbeInterval, t.C, stopCh, m.probe)
m.tickers = append(m.tickers, t)
}
// Create a push pull ticker if needed
if m.config.PushPullInterval > 0 {
// 动作2
go m.pushPullTrigger(stopCh)
}
// Create a gossip ticker if needed
if m.config.GossipInterval > 0 && m.config.GossipNodes > 0 {
t := time.NewTicker(m.config.GossipInterval)
// 动作3
go m.triggerFunc(m.config.GossipInterval, t.C, stopCh, m.gossip)
m.tickers = append(m.tickers, t)
}
// If we made any tickers, then record the stopTick channel for
// later.
if len(m.tickers) > 0 {
m.stopTick = stopCh
}
}
1) 动作1 probe
周期性的探测集群中状态为alive和suspect的节点
每个周期只探测 1个节点
2) 动作2 pushpull
周期性的从已知的alive的集群节点中选1个节点进行push/pull交换信息
交换的信息包含2种
a) 集群信息
b) 用户自定义的状态信息,需要1个实现Delegate接口的struct(请阅读参考资料2)
config.go
type Config struct {
// Delegate and Events are delegates for receiving and providing
// data to memberlist via callback mechanisms. For Delegate, see
// the Delegate interface. For Events, see the EventDelegate interface.
//
// The DelegateProtocolMin/Max are used to guarantee protocol-compatibility
// for any custom messages that the delegate might do (broadcasts,
// local/remote state, etc.). If you don't set these, then the protocol
// versions will just be zero, and version compliance won't be done.
Delegate Delegate
...
}3) 动作3 gossip
不要被函数名欺骗了,其实它是广播所有处于dead的节点(只广播一次)
3.3 注意
这里需要说明的是
1)广播其实也是一种Gossip,发布者并不把消息发给集群中的每一个节点,而是随机挑选n个(默认是3个),将消息发送出去
2)处于dead状态的节点,仍然会被保留在集群信息中一段时间,以便Push/Pull的时候,这个状态能够被扩散出去
4. 关于配置种子节点的说明
看一种极端情况,集群中有A、B、C 3个几点
A为种子节点
B、C为普通节点
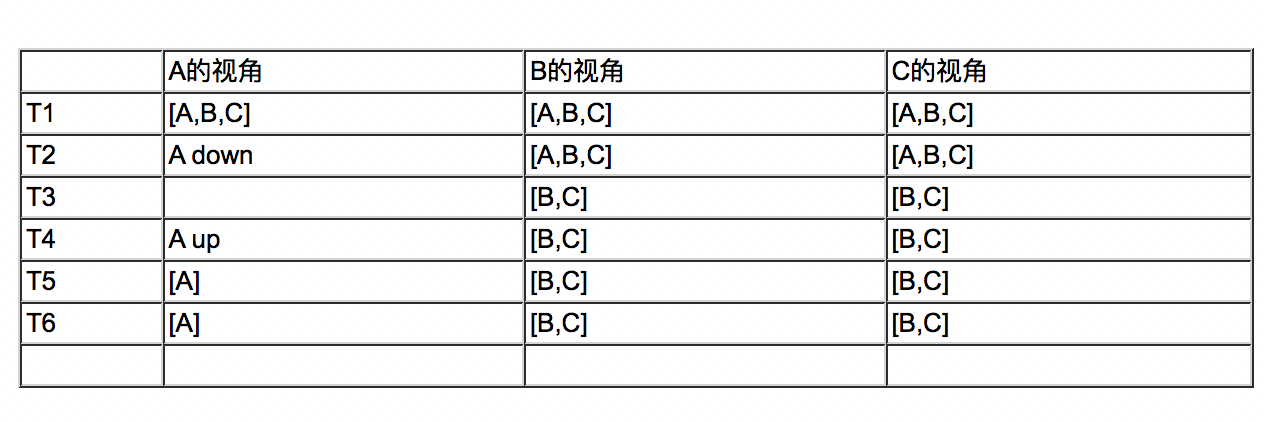
表格中是节点A、B、C在不同时刻看到的集群的情况
T1时刻, 节点A、B、C都认为集群中有3个节点
T2时刻, 节点A down了
T3时刻, 节点B、C都认为集群中有[B,C]2个节点
T4时刻, 节点A 重新上线,但是它所已知的集群就只有[A]1个节点,节点B、C 做push/pull的时候也只会在[B、C]中选取, 因此集群分裂了
要避免这种问题,方法是多配种子节点,只要确保即使有节点down机的情况下,只要所有的种子节点不同时down机即可。
其它的Gossip实现
- Apache Gossip communicates using UDP written in Java, has support for arbitrary data and CRDT types.
- gossip-python utilizes the TCP stack and it is possible to share data via the constructed network as well.
- Smudge is written in Go and uses UDP to exchange status information; it also allows broadcasts of arbitrary data across the constructed network.
参考资料
作者: vearne
文章标题: 聊聊Gossip的一个实现
发表时间: 2018 年7月4日
文章链接: https://vearne.cc/archives/584
版权说明: CC BY-NC-ND 4.0 DEED
